Lesson Objectives - the students should be able to:
- Define Data Communications
- Enumerates and understand the functions of each components of Data Communications
- Understand Data Representations and Data Flow
- Define Networks
- Understand Distributed Processing, Network Criteria, Physical Structures, Network Models
- Enumerates the Categories of Network
- Learn Interconnection of Network: Internetwork
- Define the Internet
- Know the brief history of Internet
- Define Protocols and Standard
Lecture on Introduction to Datacommunication and Networking PPT
List of Data Communications Course Outline and Lectures
Definition of Terms
- Data communication is the transfer of data from one device to another via some form of transmission medium.
- A data communications system must transmit data to the correct destination in an accurate and timely manner.
- A network is a set of communication devices connected by media links.
- Topology refers to the physical or logical arrangement of a network. Devices may be arranged in a mesh, star, bus, or ring topology.
- An internet is a network of networks.
- The Internet is a collection of many separate networks.
- TCP/IP is the protocol suite for the Internet.
- A protocol is a set of rules that governs data communication; the key elements of a protocol are syntax, semantics, and timing.
- Standards are necessary to ensure that products from different manufacturers can work together as expected.
- Forums are special-interest groups that quickly evaluate and standardize new technologies.
- A Request for Comment (RFC) is an idea or concept that is a precursor to an Internet standard.
Five Components of Data Communications
- message
- sender
- receiver
- medium
- protocol
Different forms of information
- Text
- numbers
- images
- audio
- video
Data flow between two devices
- Simplex - Only one of the two devices on a link can transmit; the other can only receive.
- Half-duplex - Each station can both transmit and receive, but not at the same time.
- Full-duplex - Both stations can transmit and receive simultaneously.
Three criteria for an effective and efficient network
- Performance - Measured in many ways, including transit time and response time. It is evaluated by two networking metrics: throughput and delay.
- Reliability - Measured by the frequency of failure, the time it takes a link to recover from a failure, and the network's robustness in a catastrophe.
- Security - Include protecting data from unauthorized access, protecting data from damage and development, and implementing policies and procedures for recovery from breaches and data losses.
Types of Connection (Line configurations)
- Point-to-point connection - two and only two devices are connected by a dedicated link.
- Multipoint connection - three or more devices share a link.
Four Basic Topologies
- Mesh - Every device has a dedicated point-to-point link to every other device.
- Star - Each device has a dedicated point-to-point link only to a central controller, usually called a hub.
- Ring - Each device has a dedicated point-to-point connection with only the two devices on either side of it.
- Bus - One long cable acts as a backbone to link all the devices in a network.
Network Categories
- Local area network (LAN) - data communication system within a building, plant, or campus, or between nearby buildings.
- Metropolitan-area network (MAN) - data communication system covering an area the size of a town or city.
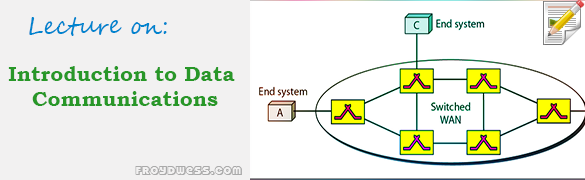
- Wide area network (WAN) - data communication system spanning states, countries, or the whole world.
Internet service providers (ISPs)
- Local
- Regional
- National
- International
Key Elements of a Protocol
- Syntax - structure or format of the data, meaning the order in which they are presented.
- Semantics - the meaning of each section of bits.
- Timing - refers to two characteristics: when data should be sent and how fast they can be sent.
Some of the organizations involved in standards creation
- ISO
- ITU-T
- ANSI
- IEEE
- EIA
Note: Lets see how well you the understand the first chapter and try answering the Multiple Choice Questions here.
List of Data Communications Lectures
credit: Behrouz A. Forouzan©2013 www.PinoyBIX.org

Post a Comment