Online Questions and Answers Topic Outline
- MCQs in DC Biasing - Field Effect Transistor
- MCQs in Fixed-Bias Configuration
- MCQs in Self-Bias Configuration
- MCQs in Voltage-Divider Biasing
- MCQs in Depletion-Type MOSFETs
- MCQs in Enhancement-Type MOSFETs
- MCQs in Summary Table
- MCQs in Combination Networks
- MCQs in Design
- MCQs in P-Channel FETs
- MCQs in Universal JFET Bias Curve
Practice Exam Test Questions
Choose the letter of the best answer in each questions.
1. What is the approximate current level in the gate of an FET in dc analysis?
- A) 0 A
- B) 0.7 mA
- C) 0.3 mA
- D) Undefined
- A) IG = ID
- B) IG = IS
- C) ID = IS
- D) IG = ID = IS
3. For the FET, the relationship between the input and output quantities is _____ due to the _____ term in Shockley's equation.
- A) nonlinear, cubed
- B) linear, proportional
- C) nonlinear, squared
4. The input controlling variable for a(n) _____ is a current level and a voltage level for a(n) _____.
- A) BJT, FET
- B) FET, BJT
- C) FET, FET
- D) BJT, BJT

- A) 0 V
- B) 8 V
- C) 4.75 V
- D) 16 V
- A) True
- B) False
7. Which of the following is (are) true of a self-bias configuration compared to a fixed-bias configuration?
- A) One of the dc supplies is eliminated.
- B) A resistor RS is added.
- C) VGS is a function of the output current ID.
- D) All of the above
8. Which of the following represents the voltage level of VGS in a self-bias configuration?
- A) VG
- B) VGS(off)
- C) VS
- D) VP

- A) 3 kΩ
- B) 3.3 kΩ
- C) 4 kΩ
- D) 5 kΩ
10. Which of the following is a false statement regarding the dc load line when comparing self-bias and voltage-divider configurations?
- A) Both are linear lines.
- B) Both cross the origin.
- C) Both intersect the transfer characteristics.
- D) Both are obtained by writing Kirchhoff's voltage law (KVL) at the input side loop.

- A) 2.400 kΩ
- B) 5.167 kΩ
- C) 6.167 kΩ
- D) 6.670 kΩ

- A) 0 V
- B) 0.35 V
- C) 3.8 V
- D) 33.5 V
13. Which of the following describe(s) the difference(s) between JFETs and depletion-type MOSFETs?
- A) VGS can be positive or negative for the depletion-type.
- B) ID can exceed IDSS for the depletion-type.
- C) The depletion-type can operate in the enhancement mode.
- D) All of the above
14. At what value of RS does the circuit switch from depletion mode to enhancement mode?

- A) 250 Ω
- B) 500 Ω
- C) 10 MΩ
- D) None of the above

- A) 10 MΩ`
- B) 100 MΩ
- C) 110 MΩ
- D) 220 MΩ
16. Depletion-type MOSFETs do not permit operating points with positive values of VGS and levels of ID that exceed IDSS.
- A) True
- B) False
17. For what value of RS can the depletion-type MOSFETs operate in enhancement mode?

- A) 2.4 kΩ
- B) 5 kΩ
- C) 6.2 kΩ
- D) None of the above

- A) 3.5 V
- B) 4.86 V
- C) 7.14 V
- D) 10 V

- A) 0 V
- B) 20 V
- C) 30 V
- D) 40 V

- A) 0 V, 0 V
- B) 5 V, 5 V
- C) 10 V, 10 V
- D) 20 V, 20 V

- A) 23.0 V
- B) 17.0 V
- C) 4.6 V
- D) 12.4 V
22. Specification sheets typically provide the value of the constant k for enhancement-type MOSFETs.
- A) True
- B) False

- A) 0 V
- B) 6 V
- C) 16 V
- D) 11 V

- A) 0 V
- B) 2 V
- C) 3 V
- D) 5.34 V
25. Given the values of VDQ and IDQ for this circuit, determine the required values of RD and RS.

- A) 2 kΩ, 2 kΩ
- B) 1 kΩ, 5.3 kΩ
- C) 3.2 kΩ, 400 Ω
- D) 2.5 kΩ, 5.3 kΩ

- A) 0 kΩ
- B) 1.68 kΩ
- C) 6.81 kΩ`
- D) 8.5 kΩ

- A) 2 kΩ
- B) 3 kΩ
- C) 3.5 kΩ
- D) 4.13 kΩ
28. In the design of linear amplifiers, it is good design practice to choose operating points that do not crowd the saturation level or cutoff regions.
- A) True
- B) False
29. Seldom are current levels measured since such maneuvers require disturbing the network structure to insert the meter.
- A) True
- B) False
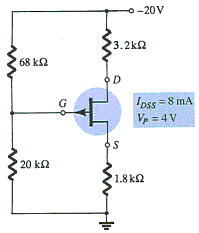
- A) –3 V
- B) 3 V
- C) –4 V
- D) 4 V

- A) 1.2 mA, –1.8 V
- B) 1.5 mA, –1.5 V
- C) 2.0 mA, –1.2 V
- D) 3.0 mA, –0.8 V

- A) 1.0 V
- B) 1.50 V
- C) 2.56 V
- D) 3.58 V
33. On the universal JFET bias curve, the vertical scale labelled _____ can, in itself, be used to find the solution to _____ configurations.
- A) m, fixed-bias
- B) M, fixed-bias
- C) M, voltage-bias
- D) m, voltage-bias
34. Through proper design, a ______ can be introduced that will affect the biasing level of a voltage-controlled JFET resistor.
- A) photodiode
- B) thermistor
- C) laser diode
- D) Zener diode
35. For the noninverting amplifier, one of the most important advantages associated with using a JFET for control is the fact that it is _____ rather than _____ control.
- A) dc, ac
- B) ac, dc
Fill-in-the-blanks Questions
1. For the field-effect transistor, the relationship between the input and the output quantities is _____.
- A) linear
- B) nonlinear
- C) 3rd degree
- D) None of the above
- A) resistor
- B) current
- C) voltage
- D) All of the above
3. The controlled variable on the output side of an FET transistor is a _____ level.
- A) current
- B) voltage
- C) resistor
- D) None of the above
4. For _____, Shockley's equation is applied to relate the input and the output quantities.
- A) JFETs
- B) depletion-type MOSFETs
- C) enhancement-type MOSFETs
- D) JFETs and depletion-type MOSFETs
5. The coupling capacitors are _____ for the dc analysis and _____________ for the ac analysis.
- A) open-circuit, low impedance
- B) short-circuit, low impedance
- C) open-circuit, high impedance
- D) None of the above
6. In a fixed-bias configuration, the voltage level of VGS is equal to _____.
- A) VS
- B) VG
- C) VGS(off)
- D) VP
7. The ratio of current ID to IDSS is equal to _____ for a fixed-bias configuration.
- A) 0
- B) 0.25
- C) 0.5
- D) 1
8. When plotting the transfer characteristics, choosing VGS = 0.5VP will result in a drain current level of _____ IDSS.
- A) 0
- B) 0.25
- C) 0.5
- D) 1
9. The dc load line is drawn using the equation obtained by applying Kirchhoff's voltage law (KVL) at _____ side loop(s) of the circuit.
- A) the output
- B) the input
- C) both the input and output
- D) None of the above
10. The slope of the dc load line in a self-bias configuration is controlled by _____.
- A) VDD
- B) RD
- C) RG
- D) RS
11. _____ levels of RS result in _____ quiescent values of ID and _____ negative values of VGS.
- A) Increased, lower, less
- B) Increased, higher, less
- C) Increased, higher, more
- D) Increased, less, lower
12. The slope of the dc load line in a voltage-divider is controlled by _____.

- A) R1
- B) R2
- C) RS
- D) All of the above
13. In a depletion-type MOSFET, the transfer characteristic rises _____ as VGS becomes more positive.
- A) less rapidly
- B) more rapidly
- C) the same
- D) None of the above
14. In _____ configuration(s) a depletion-type MOSFET can operate in enhancement mode.
- A) self-bias
- B) fixed-bias with no VGG
- C) voltage-divider
- D) None of the above
15. In an enhancement-type MOSFET, the drain current is zero for levels of VGS less than the _____ level.
- A) VGS(Th)
- B) VGS(off)
- C) VP
- D) VDD
16. Specification sheets typically provide _____ for enhancement-type MOSFETs.
- A) the threshold voltage VGS(Th)
- B) a level of drain current ID(on)
- C) an ID(on)
- D) All of the above
17. In a feedback-bias configuration, the slope of the dc load line is controlled by _____.
- A) RG
- B) RD
- C) VDG
- D) None of the above
18. For R2 smaller than _____ kΩ the voltage VD is equal to VDD = 16 V.

- A) 3.75
- B) 5
- C) 12.0
- D) 24
- A) Dc conditions
- B) Level of amplification
- C) Signal strength
- D) All of the above
20. In a JFET, the level of _____ is limited to values between 0 V and –VP.
- A) VSQ
- B) VDGQ
- C) VDSQ
- D) VGSQ
21. The level of VDS is typically between _____ % and _____ % of VDD.
- A) 0, 100
- B) 10, 90
- C) 25, 75
- D) None of the above
22. In a universal JFET bias curve, the vertical scale labeled m is used to find the solution to the _____ configuration.
- A) fixed-bias
- B) self-bias
- C) voltage-divider
- D) None of the above
23. In a universal JFET bias curve, the vertical scale labeled M is used for finding the solution to the _____ configuration.
- A) fixed-bias
- B) self-bias
- C) voltage-divider
- D) None of the above
25. In p-channel FETs, the level of VGS is _____ while the level of VDS is _____.
- A) negative, negative
- B) positive, positive
- C) negative, positive
- D) positive, negative
Check your work.
Complete List of Chapter Quiz in Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory
credit: Robert L. Boylestad© 2014 www.PinoyBIX.org


Post a Comment